Serotonin: What It Does and Why You Should Care
Low or high serotonin isn’t just a mood label. It affects sleep, appetite, digestion, pain sensitivity, and even sexual function. Knowing how serotonin works helps you spot problems sooner and avoid risky drug interactions.
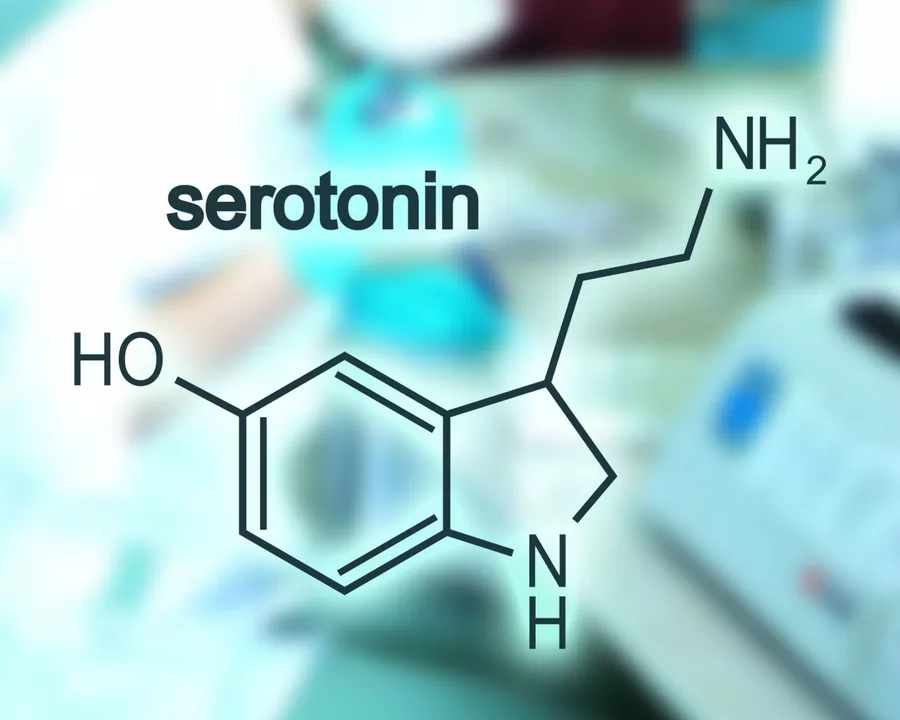
Serotonin is a chemical messenger your brain and gut use to talk to the rest of your body. About 90% of it lives in the gut, where it helps control bowel movements and digestion. The rest acts in the brain to influence mood, sleep cycles, and impulse control.
How serotonin affects mood and the body
In the brain, serotonin helps stabilize mood and calm anxiety. Medicines called SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) raise serotonin levels by blocking its reabsorption, which can ease depression and some anxiety disorders. But raising serotonin isn’t always harmless—too much can trigger a dangerous condition called serotonin syndrome. Watch for sudden agitation, fast heart rate, high fever, muscle rigidity, or confusion. That needs emergency care.
On the body side, serotonin directs gut movement and influences appetite. Low serotonin can show up as insomnia or sleep disruption, cravings for carbs, constipation or IBS-type symptoms, and higher pain sensitivity. High levels can cause nausea, diarrhea, or restlessness.
Simple, safe ways to support healthy serotonin
Want practical steps you can try right now? Start with sleep and movement. Regular exercise—especially brisk walking, cycling or short bursts of activity—helps your brain make and release serotonin. Get daylight in the morning to support natural rhythm and mood. Aim for steady sleep: consistent bedtimes make a big difference.
Diet matters but it’s not a magic fix. Foods high in tryptophan (turkey, eggs, cheese, soy, nuts) give your body the building blocks for serotonin, but they work best with carbs that help tryptophan reach the brain. Don’t rely on supplements alone. 5-HTP and tryptophan supplements can boost serotonin but also raise the risk of interactions—talk to your doctor before trying them, especially if you take prescription antidepressants.
Be careful with drug combinations. Mixing SSRIs with MAO inhibitors, certain pain meds (like tramadol), triptans for migraines, or herbal products like St. John’s wort can increase the chance of serotonin syndrome. Always tell providers about all meds and supplements you use.
If low mood or anxiety is affecting daily life, therapy and lifestyle changes are first-line options. Medications can help when recommended by a clinician. If you notice sudden confusion, a rapid heartbeat, high fever, severe tremor, or loss of coordination after starting or changing a drug, get emergency help and mention serotonin syndrome.
Want related reads? This tag groups articles about medicines, interactions, and lifestyle tips that touch on serotonin—like antidepressant guides, drug interaction warnings, and safer strategies to manage mood and sleep. Browse the posts below to find practical, easy-to-use info for your situation.
The Relationship Between Buspirone and Serotonin: What You Need to Know
In today's post, I'll be discussing the relationship between Buspirone and Serotonin, which is important for those considering this medication. Buspirone is an anti-anxiety drug that works by affecting the levels of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter responsible for regulating mood, anxiety, and happiness. By increasing serotonin levels, Buspirone helps to alleviate anxiety symptoms without the risk of addiction or dependence. It's essential to consult with your doctor before starting Buspirone to ensure it's the right choice for your specific needs.