Buspirone: Quick Guide to Uses, Dosing, and Side Effects
Buspirone is a prescription medication for generalized anxiety disorder and for short-term relief of anxiety symptoms. It’s not a benzodiazepine, so it usually causes less drowsiness and has a lower risk of dependence. People choose buspirone when they need ongoing anxiety control without the sedative effects of benzodiazepines.
How buspirone works and who it's for
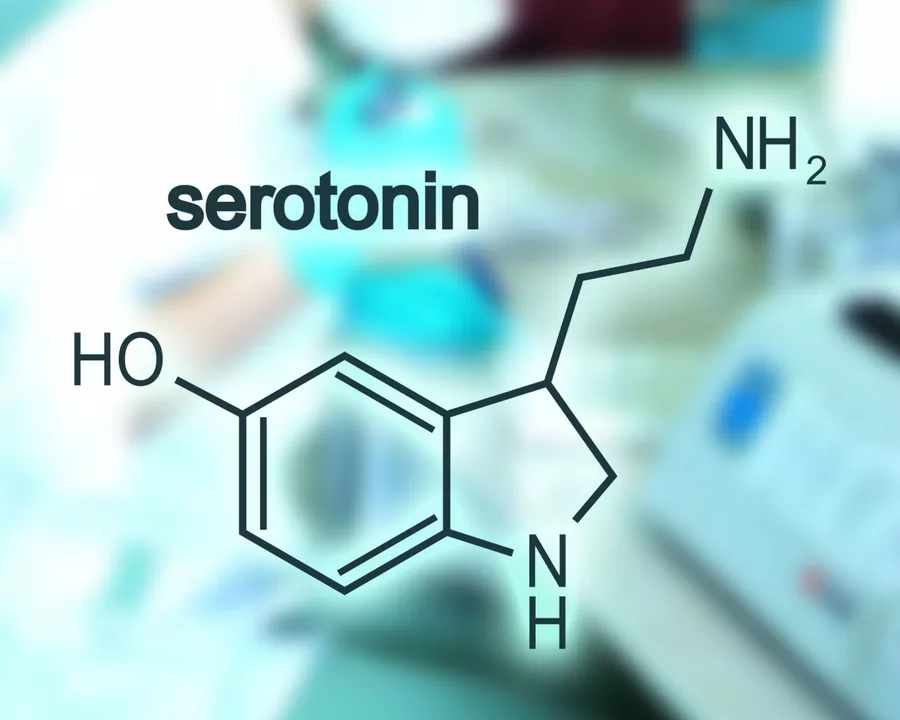
Buspirone works by acting on serotonin receptors in the brain, mainly as a 5-HT1A partial agonist. That sounds technical, but the takeaway is simple: it calms anxious thoughts without heavy sedation. Doctors often prescribe it for generalized anxiety disorder, worry that interferes with daily life, or when benzodiazepines are undesirable. It can take two to four weeks to notice full benefits, so patience matters.
Dosing, side effects, and safe use
Typical starting doses are 5 to 7.5 mg twice a day, with gradual increases. Many people end up on 15 to 30 mg per day split into two or three doses; maximum daily dose is usually 60 mg. Take buspirone consistently—same times each day—because it needs steady blood levels. Do not crush extended-release tablets unless your pharmacist says it’s okay.
Common side effects include dizziness, nausea, headache, and nervousness. These often ease after a week or two. More serious issues are rare but include severe allergic reactions or movement problems; tell your doctor if you notice sudden muscle stiffness, fever, or unusual behavior. Avoid drinking large amounts of alcohol while on buspirone; alcohol can increase dizziness and reduce effectiveness.
Watch for drug interactions. Buspirone is mainly broken down by CYP3A4 in the liver, so strong inhibitors like ketoconazole or itraconazole can raise buspirone levels. Some antibiotics and heart medications also affect levels, so tell your doctor about everything you take. Combining buspirone with MAO inhibitors is not recommended. If you’re on antidepressants, especially SSRIs, your doctor will watch for signs of serotonin syndrome—this is uncommon but serious.
Pregnant or breastfeeding? Data is limited. Talk with your prescriber about risks and benefits before starting buspirone. For older adults, doctors may start at a lower dose and increase slowly to reduce side effects.
Stopping buspirone is generally easier than stopping benzodiazepines, but sudden changes are still not ideal. If you want to stop, work with your doctor to taper the dose over a few weeks to avoid rebound anxiety.
Need to buy buspirone online? Only use licensed pharmacies and expect to provide a valid prescription. Avoid sites that sell controlled meds without a prescription—those are risky. If you have questions about dosing, side effects, or interactions, ask your pharmacist or prescriber; they can give advice tailored to your situation.
Keep buspirone stored at room temperature away from moisture and heat. Carry a current medicine list when you travel. Be cautious with driving or heavy machines until you know how it affects you. Combining buspirone with therapy or lifestyle changes like exercise and sleep hygiene often improves results. Talk openly with your healthcare team if symptoms change or worsen.
The Relationship Between Buspirone and Serotonin: What You Need to Know
In today's post, I'll be discussing the relationship between Buspirone and Serotonin, which is important for those considering this medication. Buspirone is an anti-anxiety drug that works by affecting the levels of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter responsible for regulating mood, anxiety, and happiness. By increasing serotonin levels, Buspirone helps to alleviate anxiety symptoms without the risk of addiction or dependence. It's essential to consult with your doctor before starting Buspirone to ensure it's the right choice for your specific needs.