Skeletal Muscle Conditions: Treatments, Research & Insights
When working with skeletal muscle conditions, a group of disorders that weaken or damage the muscles used for movement and stability. Also known as muscle diseases, they affect millions of people worldwide. These conditions range from inherited disorders to age‑related loss, and each one has its own set of challenges. Below we break down the most common types and the tools doctors use to combat them.
One major category is muscular dystrophy, a genetic disease that causes progressive muscle degeneration. Another is sarcopenia, the natural loss of muscle mass and strength that comes with aging. Both share the core problem of reduced muscle function, but their causes and treatment paths differ. Understanding the distinction helps you pick the right approach.
Modern research points to two promising families of therapies. myostatin inhibitors, drugs that block the myostatin protein which limits muscle growth aim to boost muscle size and strength. Meanwhile, stem cell therapy, the use of engineered cells to repair or replace damaged muscle tissue targets the root cause by regenerating healthy fibers. Both approaches are still emerging, but early trials show real potential.
These treatments don’t work in isolation. Physical therapy, proper nutrition, and regular exercise remain essential pillars. For sarcopenia, resistance training can double the benefit of a myostatin inhibitor. In muscular dystrophy, gene‑editing tools like CRISPR are being paired with stem cell transplants to correct the underlying mutation. The synergy between medicine and lifestyle creates the most durable outcomes.
Clinicians also need to weigh safety. Myostatin blockers can cause unwanted tissue growth if dosed too high. Stem cell procedures carry risks of immune reaction or improper cell differentiation. Monitoring blood markers and imaging scans helps catch issues early. Patients should discuss the risk‑benefit profile with a specialist who tracks the latest trial data.
Insurance coverage is another practical hurdle. Because many of these therapies are still classified as experimental, they often fall under clinical trial programs or compassionate use. Knowing the right trial registries and hospital programs can open doors to affordable care. A good pharmacist can also help navigate discount cards and patient assistance plans.
From a research perspective, the field is moving fast. Gene‑therapy vectors that deliver healthy copies of the dystrophin gene are in late‑stage trials for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. At the same time, small‑molecule myostatin inhibitors are gaining FDA fast‑track status for rare muscle‑wasting disorders. These advances illustrate a clear trend: targeted molecular solutions are becoming the backbone of muscle disease management.
For patients, staying informed is key. Ask your doctor about the latest trial results, ask whether you’re a candidate for a stem‑cell infusion, and ask how lifestyle changes can enhance drug efficacy. Knowledge empowers you to make choices that match your goals and your health profile.
Understanding these skeletal muscle conditions helps you choose the right therapy, plan your care, and stay ahead of new developments. Below you’ll find a curated list of articles that dive deep into specific drugs, emerging technologies, and real‑world tips for living with muscle disorders.
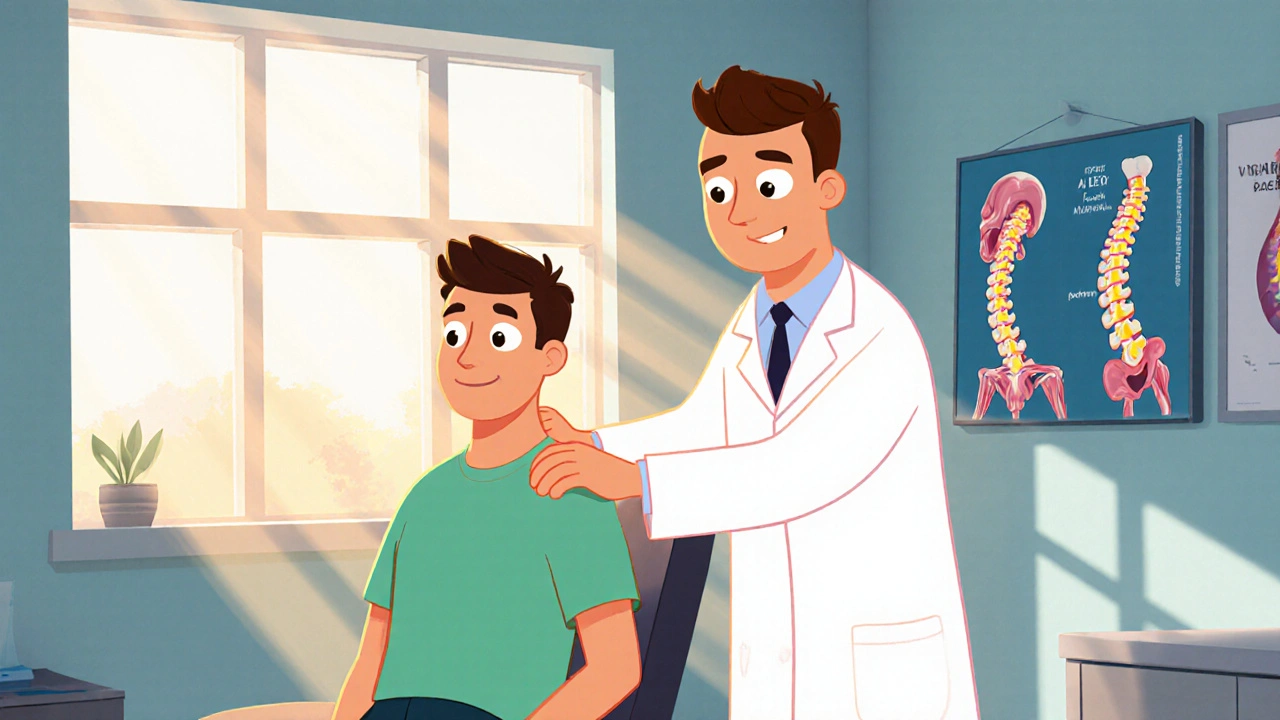
How Chiropractic Care Helps Manage Skeletal Muscle Conditions
Explore how chiropractic care can relieve muscle pain, improve range of motion, and support rehab for skeletal muscle conditions. Learn techniques, evidence, and when to seek a chiropractor.