Understanding Eczema and Its Causes
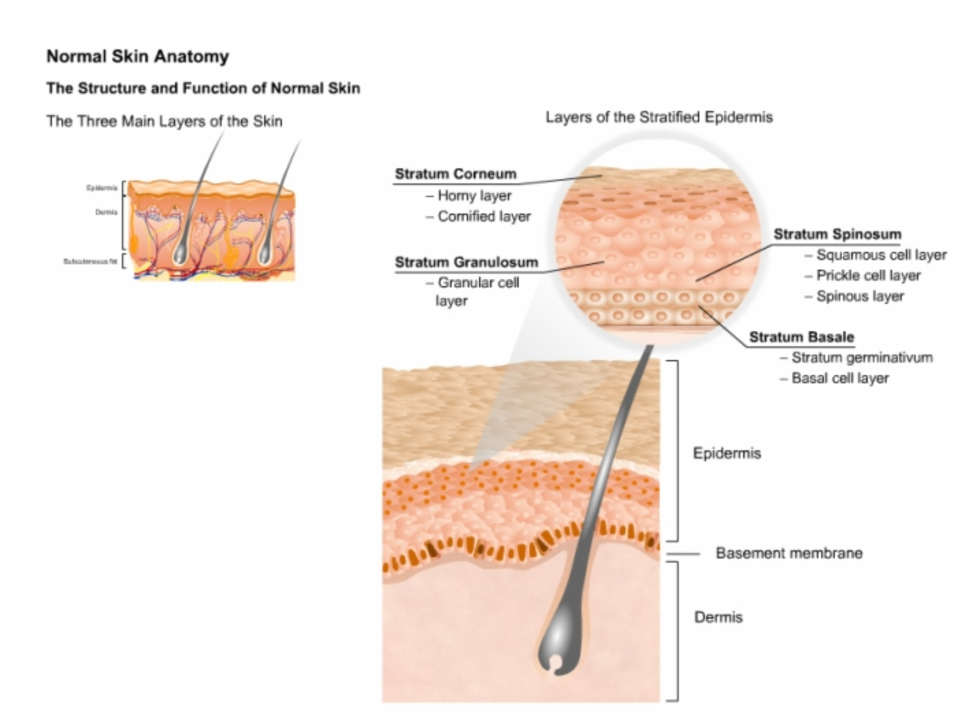
Eczema is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed patches of skin. Although there is no known cure for eczema, understanding its causes can help us manage and prevent skin infections associated with this condition.
The exact cause of eczema is still unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some research suggests that people with eczema have a weakened skin barrier, which makes it easier for allergens and irritants to penetrate the skin and cause inflammation. Additionally, individuals with eczema may have an overactive immune system that reacts strongly to these irritants, leading to the red, itchy rash that is characteristic of the condition.
Various Types of Skin Infections Associated with Eczema
People with eczema are more susceptible to skin infections due to their compromised skin barrier and overactive immune system. There are several types of skin infections that can occur in individuals with eczema, including bacterial, viral, and fungal infections.
Bacterial infections, such as impetigo and cellulitis, are common in people with eczema. Staphylococcus aureus is a type of bacteria that is often found on the skin of individuals with eczema and can cause skin infections if it enters through cracks or open sores. Viral infections, like herpes simplex virus and molluscum contagiosum, can also affect people with eczema and lead to more severe complications. Lastly, fungal infections, such as ringworm and candidiasis, can develop in the moist, warm areas of the skin affected by eczema.
Recognizing Symptoms of Skin Infections in Eczema Patients
It is crucial to recognize the symptoms of skin infections in people with eczema as early treatment can help prevent complications and worsening of the condition. Some common signs of skin infections include increased redness, swelling, warmth, and pus or discharge from the affected area.
In addition to these symptoms, individuals with bacterial infections may experience fever and chills, while those with viral infections may develop blisters or ulcers on the skin. Fungal infections often present as circular, red, and scaly patches on the skin. If you or someone you know with eczema is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Preventing Skin Infections in People with Eczema
Preventing skin infections is an important aspect of managing eczema. There are several steps individuals with eczema can take to reduce their risk of developing skin infections, such as maintaining good hygiene, avoiding known triggers, and keeping the skin moisturized.
Daily bathing with a gentle, fragrance-free cleanser can help remove bacteria and other irritants from the skin. After bathing, it is important to apply a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer to help repair the skin barrier and lock in moisture. Additionally, avoiding known triggers, such as allergens and irritants, can help prevent eczema flare-ups and reduce the risk of skin infections.
Importance of Proper Wound Care in Eczema Patients
Proper wound care is essential for individuals with eczema to prevent skin infections and promote healing. This includes keeping the affected area clean and dry, applying a topical antibiotic ointment if recommended by a healthcare professional, and covering the wound with a sterile bandage.
It is also important to avoid scratching or picking at the affected area, as this can introduce bacteria and other pathogens into the wound and increase the risk of infection. If you notice any signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
How Stress and Anxiety Can Exacerbate Eczema and Skin Infections
Stress and anxiety can have a significant impact on the severity and frequency of eczema flare-ups and skin infections. When we experience stress, our bodies release certain hormones that can cause an inflammatory response in the skin, worsening eczema symptoms.
Additionally, stress can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for our bodies to fight off infections. Therefore, finding effective ways to manage stress and anxiety can help improve eczema symptoms and reduce the risk of skin infections. Some possible stress-reduction techniques include regular exercise, practicing mindfulness and meditation, and seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professional.
Treatment Options for Skin Infections in Eczema Patients
Treatment for skin infections in individuals with eczema depends on the type and severity of the infection. Bacterial infections are typically treated with oral or topical antibiotics, while antiviral medications may be prescribed for viral infections. Fungal infections are usually treated with antifungal creams or oral medications.
In addition to treating the infection, healthcare professionals may also recommend steps to manage eczema symptoms and prevent future infections. This may include using a topical corticosteroid to reduce inflammation and itchiness, as well as adopting a consistent skincare routine to maintain a healthy skin barrier.
Seeking Professional Help for Eczema and Skin Infections
If you or someone you know is struggling with eczema and skin infections, it is important to seek professional help. A healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist, can provide a proper diagnosis, recommend appropriate treatments, and offer guidance on managing eczema and preventing future infections.
Remember, early intervention is key to preventing complications and improving the overall quality of life for individuals with eczema. Don't hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional if you suspect a skin infection or need help managing your eczema symptoms.
tim jeurissen
May 11, 2023 AT 19:48The compromised skin barrier in eczema literally invites pathogenic colonisation; you can't blame Staph aureus for exploiting those micro‑fissures, but you can mitigate it with diligent emollient therapy and barrier‑repair formulations. Proper hygiene, while essential, must avoid over‑washing that strips lipids and exacerbates transepidermal water loss.
lorna Rickwood
May 19, 2023 AT 14:28it's kinda like the skin is a castle and the eczema cracks are the moats missing, so bacteria just stroll in, no?
Mayra Oto
May 27, 2023 AT 09:08From a cultural perspective, many societies still treat eczema as a cosmetic issue rather than a medical one, which delays proper infection prevention. Education campaigns that respect local beliefs can improve early treatment uptake.
S. Davidson
June 4, 2023 AT 03:48Let’s be clear: the immunological dysregulation in eczema isn’t just a flaky inconvenience; it predisposes patients to Staph colonisation, herpes simplex outbreaks, and even opportunistic fungal growth. Topical corticosteroids reduce inflammation but can also thin the skin, so you need to balance potency with barrier support. Moisturizers with ceramides restore lipid architecture, lowering microbial adhesion. Antibiotic stewardship is critical; overuse selects for MRSA, which then becomes a chronic problem. Probiotic skin care may offer a future avenue, yet data remain preliminary. In short, a multifaceted, interdisciplinary approach is non‑negotiable.
Haley Porter
June 11, 2023 AT 22:28When we examine the pathophysiology of eczema through a lens of barrier dysfunction, immune hyperreactivity, and microbiome imbalance, a tapestry of interrelated mechanisms emerges that underpins the heightened susceptibility to cutaneous infections. First, the epidermal lipid matrix is compromised, leading to increased transepidermal water loss and permitting facile ingress of microbial pathogens. Second, the overexpression of Th2 cytokines such as IL‑4 and IL‑13 not only drives pruritus but also down‑regulates antimicrobial peptides like cathelicidin, creating an immunological vacuum that Staphylococcus aureus readily exploits. Third, colonisation by S. aureus itself can exacerbate inflammation via superantigen production, establishing a vicious feedback loop. Moreover, viral agents like herpes simplex virus find a receptive niche in disrupted skin, often presenting as herpetic eczema herpeticum, a potentially life‑threatening condition if not promptly treated with antiviral therapy. Fungal organisms, particularly Candida spp. and dermatophytes, thrive in the moist intertriginous zones characteristic of eczema, where occlusion and maceration reduce local pH and favor hyphal growth. The clinical sequelae range from impetiginous crusting to secondary cellulitis, each demanding a tailored pharmacologic regimen-topical mupirocin for localized bacterial involvement, oral cephalexin for deeper tissue infection, and systemic azoles for recalcitrant dermatophytosis. Beyond pharmacotherapy, rigorous skin‑care regimens anchored in fragrance‑free, emollient‑rich moisturizers replenish the lipid barrier, attenuating xerosis and reducing fissure formation. Regular bathing with mild, non‑ionic surfactants removes surface debris without stripping essential lipids, and immediate post‑bath application of occlusive ointments locks in moisture, reinforcing barrier integrity. Adjunctive strategies such as low‑dose systemic immunomodulators (e.g., dupilumab) have demonstrated efficacy in reducing both eczema severity and colonisation density, though cost considerations remain a barrier for many patients. Finally, psychosocial stressors potentiate the HPA‑axis, elevating cortisol and catecholamines that further impair cutaneous immunity; mind‑body interventions, including mindfulness‑based stress reduction, can thus indirectly diminish infection risk. In summary, the interplay of barrier compromise, immune dysregulation, microbial colonisation, and psychosocial factors creates a perfect storm for skin infections in eczema, necessitating an integrated therapeutic approach that addresses each component holistically.
Samantha Kolkowski
June 19, 2023 AT 17:08i think that was a solid breakdown, just remember to keep the skin moisturized and dont overdo the steroids i guess.
Nick Ham
June 27, 2023 AT 11:48Eczema patients are basically walking petri dishes for bacteria; cut the crap and use proper topical antibiotics.
Jennifer Grant
July 5, 2023 AT 06:28Well, you see, the thing about antibiotics is that they're like a double‑edged sword, right? On one hand, they can clear up a nasty staph infection that’s been lurking in those eczema cracks-very effective, very fast. On the other hand, if you overprescribe them, you end up creating resistant strains, which is a whole other nightmare. So it’s a delicate balance, like walking a tightrope over a pit of lava. The key is targeted therapy: culture the wound, identify the pathogen, then pick the right drug. Broad‑spectrum sprays might feel convenient, but they’re like using a hammer to crack a walnut-overkill and messy. And don’t forget the adjunctive care: moisturizers, barrier creams, and maybe even probiotic wipes to repopulate the skin with good bacteria. That’s the nuanced approach you need, not just slapping on any ointment you find on the shelf.
Kenneth Mendez
July 13, 2023 AT 01:08They’re hiding the truth about eczema infections.
Gabe Crisp
July 20, 2023 AT 19:48While conspiracy theories are entertaining, the medical community has extensive peer‑reviewed evidence on eczema management; dismissing it undermines patient care.
Paul Bedrule
July 28, 2023 AT 14:28One could argue that eczema exemplifies the dialectic between the body's innate defense mechanisms and environmental provocations, a true embodiment of the microcosm‑macrocosm interplay.
yash Soni
August 5, 2023 AT 09:08Oh great, another “expert” trying to sell their patented cream-sure, because nothing says “science” like a snarky Instagram post. Meanwhile, real patients are stuck battling infections that could be avoided with basic hygiene and decent moisturizers. But hey, why bother with evidence when you can brag about your “unique formula” that probably contains more preservatives than actual active ingredients?
Emily Jozefowicz
August 13, 2023 AT 03:48Great rundown! Just a reminder to keep the tone inclusive-skin conditions don’t discriminate, and neither should our advice.
Franklin Romanowski
August 20, 2023 AT 22:28I totally agree. It can be overwhelming, but remember you’re not alone-support groups and gentle skin‑care routines can make a huge difference in daily life.
Brett Coombs
August 28, 2023 AT 17:08Everyone’s hiding the fact that eczema is a government experiment.
John Hoffmann
September 5, 2023 AT 11:48While creative, there’s no credible data supporting such claims; reputable sources confirm eczema’s multifactorial etiology rooted in genetics and environment.
Shane matthews
September 13, 2023 AT 06:28Thanks for the thorough info-just a quick tip: when applying moisturizer, use the “finger‑palm” method to gently spread without rubbing, which can further irritate the skin.
Rushikesh Mhetre
September 21, 2023 AT 01:08Awesome tip! And remember to seal in that moisture within 3 minutes of bathing; the skin is most receptive then, making your routine even more effective.