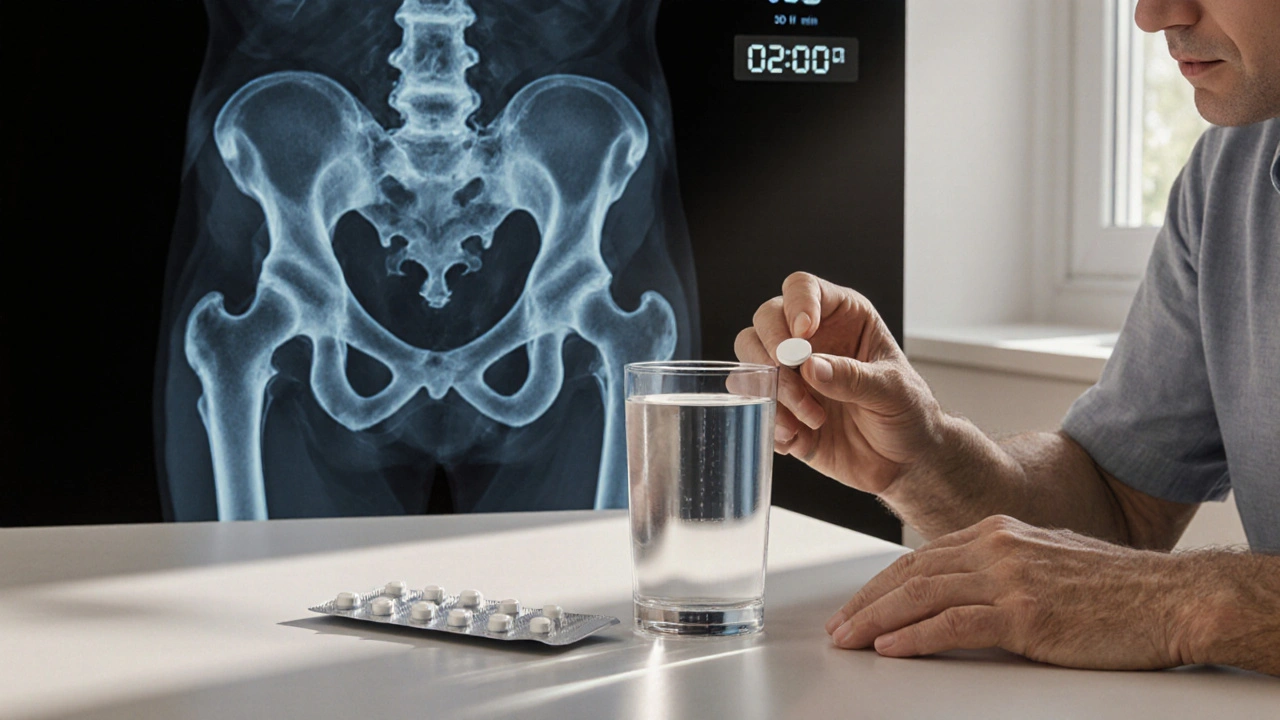
Paget's disease medication
When dealing with Paget's disease medication, drugs used to control abnormal bone remodeling in Paget's disease. Also known as osteitis deformans treatment, it helps reduce bone pain, normalize bone turnover, and improve quality of life. Understanding the range of medicines available can feel overwhelming, but breaking them into clear groups makes the picture much easier to see.
Key drug classes and how they work
The first group most doctors reach for are bisphosphonates, agents that bind to bone and inhibit osteoclast‑mediated bone resorption. These drugs, such as alendronate or risedronate, directly slow down the cells that break down bone, which in Paget's disease are over‑active. By doing that, they lower the elevated alkaline phosphatase levels and often quiet the characteristic bone pain. A typical semantic triple here is: Paget's disease medication includes bisphosphonates, which reduce bone turnover.
The second major class is denosumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets RANKL to prevent osteoclast formation. Unlike bisphosphonates, denosumab is given as an injection every six months and works by blocking the signal that tells osteoclasts to mature. This results in a rapid drop in bone turnover markers and can be a good alternative for patients who cannot tolerate oral bisphosphonates. Here we see another triple: Denosumab reduces osteoclast activity, complementing the action of Paget's disease medication.
A third, older option is calcitonin, a hormone that directly inhibits osteoclasts and provides quick pain relief. It is usually given by nasal spray or injection and works faster than bisphosphonates, but its effect wanes after a few months, so it is often used for short‑term symptom control while other treatments take effect. This connects as: Calcitonin offers rapid pain relief, bridging the gap until longer‑acting Paget's disease medication kicks in.
Beyond drugs that target bone cells, managing the discomfort that comes with Paget's disease is essential. pain management, strategies that combine analgesics, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes plays a supportive role. Simple over‑the‑counter NSAIDs can help with mild aches, while stronger prescription opioids are reserved for severe flare‑ups. Physical therapy keeps the affected bones mobile and reduces the risk of fractures. Together, these approaches form a holistic triple: Effective Paget's disease medication plus pain management improves overall patient outcomes.
When choosing a therapy, doctors look at several attributes: the speed of symptom relief, the duration of action, side‑effect profile, and the patient's overall health. For example, bisphosphonates may cause esophageal irritation, so they require the patient to stay upright after swallowing. Denosumab can lower calcium levels, so supplements might be needed. Calcitonin is generally well‑tolerated but may cause nasal irritation when used as a spray. These attribute‑value pairs help clinicians tailor treatment to each individual.
Another practical factor is monitoring. Blood tests for alkaline phosphatase give a quick read on how well the medication is working. Imaging studies, like bone scans, show changes in the affected regions over months. Regular follow‑ups let doctors adjust doses or switch drugs if the disease remains active. This ongoing cycle—prescribe, monitor, adjust—highlights the relationship: Paget's disease medication requires consistent monitoring to ensure effectiveness.
Understanding Paget's disease medication is the first step toward taking control of this chronic bone condition. Below you’ll find a curated list of articles that dive deeper into each drug class, compare side‑effects, offer buying guides for affordable options, and share real‑world tips for living with Paget's disease. Use the information to ask informed questions at your next appointment and to choose the therapy that fits your lifestyle best.
Didronel (Etidronate) vs Alternative Treatments: A Detailed Comparison
A comprehensive side‑by‑side review of Didronel (etidronate) versus newer bone‑health drugs, covering efficacy, dosing, side‑effects, cost and which option fits different patients.